On my Windows PC, all of my files and folders are read-only.
Why is my file marked as read-only?
The Read-only mode simply allows you to see or print a file. If a file is marked as Read-only, it means that its characteristics and attributes have been set to Read-only and you are not permitted to edit it. The system administrator or the file owner may implement this limitation. It is done to secure files and safeguard them from illegal access. In some circumstances, your antivirus may open potentially dangerous files as Read-only.
If all of your files and folders on your Windows PC are Read-only or constantly reverting to this state, there could be several causes. Here are some possible explanations:
- It’s possible that your system administrator has placed limitations on files and directories and you don’t have the necessary permissions to edit them.
- The problem could also be triggered if you use a folder lock application.
- The permissions of files and folders may have been altered as a result of a virus infestation.
- In rare circumstances, having Restricted folder access enabled under Windows Security may be the cause of this problem.
- A newly installed program may be changing folder permissions.
- Such issues can be caused by malware or ransomware.
Before attempting the repairs listed below, please ensure that your hard drive is not corrupted. Also, conduct a virus scan and eliminate any viruses or malware found on your computer. You should also run a standalone on-demand antivirus scanning to ensure that your computer is not compromised.
Improve the Performance of Your PC while Maintaining Its Security
Outbyte PC Repair
Outbyte PC Repair is a comprehensive computer repair application that was created to solve a wide variety of various system issues, clean up your drive, enhance speed, and increase both your privacy and security.
Please be aware that PC Repair is not intended to take the place of antivirus software but rather to work in conjunction with it.
On my Windows PC, all of my files and folders are set to read-only.
If all of your files and folders are Read-only or constantly reverting to Read-only mode on your Windows 11/10 PC, you can use the techniques listed below to resolve the problem.
Determine whether the problem is limited to specific files and directories.
The first thing to look for is whether the problem affects all or just a few files and folders. If you only want to edit the properties of certain files or folders, you can do so via the right-click menu. To do so, follow the instructions below:
- To begin, launch File Explorer by pressing Win+E and navigate to the location of the affected file/folder.
- Now, right-click on the file/folder and select Properties from the context menu that appears.
- Then, from the General tab, uncheck the Read-only checkbox next to the Attributes option.
- Lastly, to save your changes, click the Apply > OK option.
If you’re having this problem with all or most of your files and folders, or if your files and folders keep reverting to Read-only, try another solution from this thread.
Use an administrator account to log in.
If you are logged in with a normal or guest user account with restricted access, the problem may occur. You will be unable to edit a file or folder created using an administrator account. Alternatively, if your administrator has restricted access to the hard drive and its contents, you will only be allowed to read the files or folders. As a result, you must log in to your computer as an administrator and then attempt to access your files and directories. You can also ask your administrator for access permissions for the same.
Check that you are not using any folder lock software.
If you use folder lock software to safeguard your files and folders, such as SecretFolder, Gilisoft File Lock Pro, or HiddenDIR, it could be creating the problem. Hence, if the case applies, you just need to disable folder protection to address the problem. If the scenario does not apply to you, proceed to the next solution.
Modify the destination drive’s permissions.
Following a recent Windows update or changes to your system, the file and folder permissions may have been altered and set to Read-only. As a result, you can attempt manually altering the drive permissions to remove the Read-only limitation from your files and folders. Here’s how you do it:
To begin, launch File Explorer by pressing Win+E and navigate to the drive containing the files and folders that are causing you problems. Now, right-click on the drive and pick Properties from the context menu that appears.
Go to the Security tab in the newly opened window and press the Advanced button at the bottom of the window.
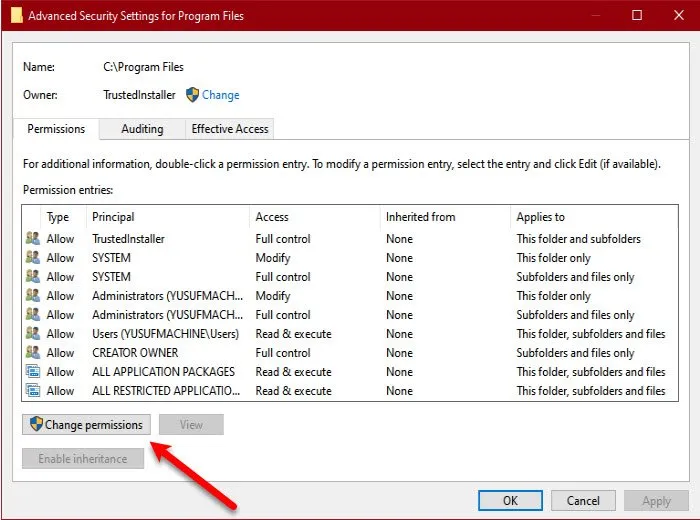
Following that, click the Modify permissions button, then select your user and press the Edit button.
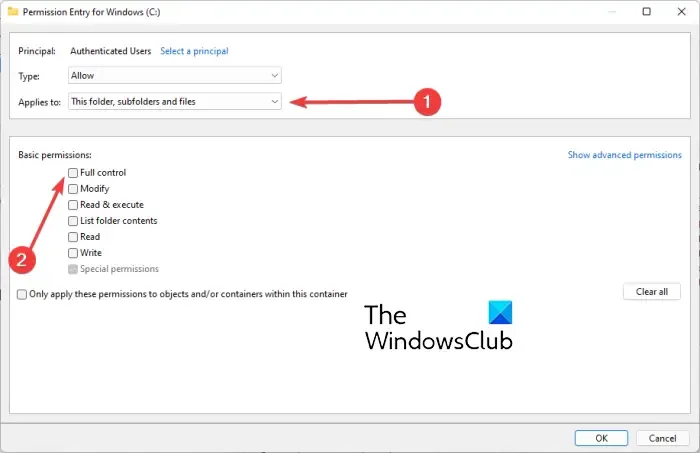
Then, select the This folder, subfolders, and files option from the Applies to: drop-down menu. Then, under Basic permissions, choose the Full control checkbox and press the OK button. Hopefully, you won’t have to deal with the same problem again.
If you have numerous users on your system, you can adjust your drive permissions as follows:
To begin, navigate to the system disk and double-click the Users folder to open it. You’ll notice a folder with your username; simply right-click on it and select Properties from the right-click context menu.
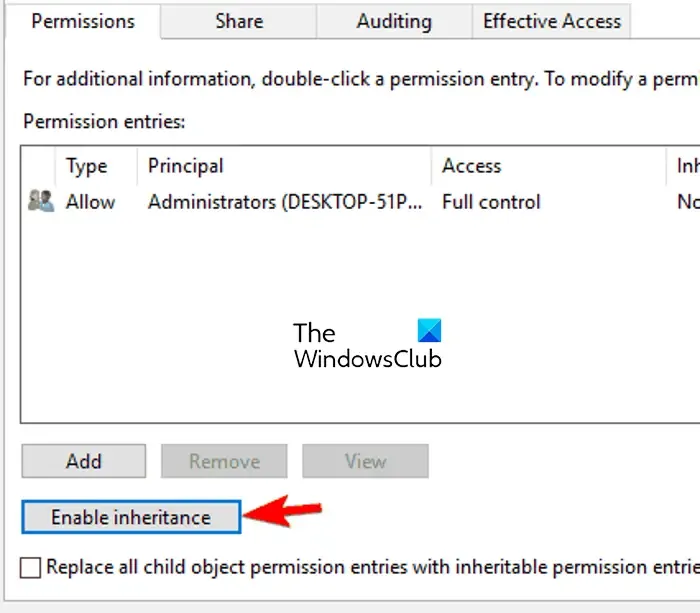
Go to the Security tab in the Properties box and choose the Advanced button. Then, to save changes, tap the Activate inheritance button and then the Apply > OK button.
Using Command Prompt, change the folder property.
You can also use Command Prompt to change the folder property. This applies if you are unable to access files and directories even when logged in as an administrator. Using Command Prompt, follow the steps below to remove the read-only attribute from folders:
To begin, launch Command Prompt as an administrator by typing cmd into the Search box, hovering the cursor over the Command Prompt program, and selecting Run as administrator.
To remove the Read-only attribute and apply system attributes, use the following command:
attrib -r +s <full path of the target folder>
For example:
attrib -r +s "C:\TWC"
Unfortunately, some folders may not work well with system attributes, in which case you can use the following command:
attrib -r -s <full path of the target folder>
For example:
attrib -r -s "C:\TWC"
Check to see if the problem has been resolved after running the command. If this doesn’t work, you can try the next solution.
Disable Restricted folder access.
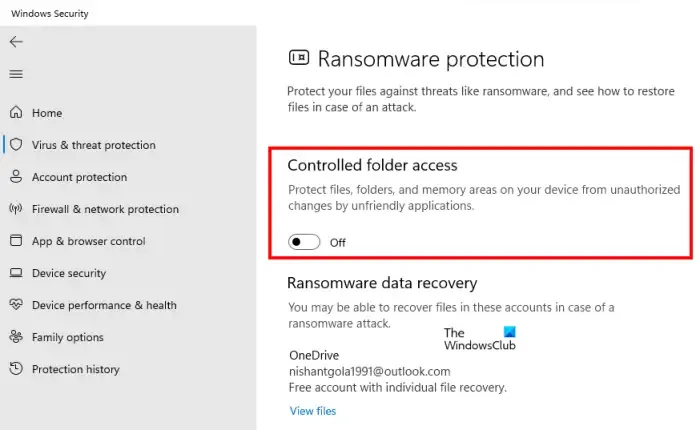
If the “folders reverting to Read-only mode” problem persists after attempting the remedies listed above, you can disable Controlled folder access on your computer. The problem could be caused by Ransomware protection that has been enabled to protect your files and folders from unauthorized access. As a result, you can disable it to resolve the problem.
Here’s how you can go about it:
- To begin, use Windows Search to find the Windows Security app.
- Go to the Virus & threat protection tab now.
- Then, in the Virus & threat protection settings section, select the Manage settings option.
- Go down to the Controlled folder access section and select Manage Controlled folder access.
- Finally, set Controlled folder access to Off to disable it.
- Finally, restart your computer to verify if the issue has been repaired.
If you still have the same issue, there are a couple more ideas you can try, so proceed to the next remedy.
Uninstall the newly installed software.
If you began experiencing this problem after installing a third-party application on your PC, it is possible that the permissions were changed by that program. Hence, uninstall any recently installed applications and verify if the problem is resolved. To do so, press Win+I to access Settings, then navigate to the Applications tab and pick the Installed programs option. Then, pick the software, click the three-dot menu button, select Uninstall, and follow the on-screen instructions. After that, restart your computer to see if the problem has been resolved.
Leave a Reply