How to Fix Inaccessible ReFS Volume After Update

ReFS, short for Resilient File System, is engineered to offer enhanced scalability and reliability compared to the conventional NTFS file system. It can handle larger volumes of local and network storage while employing a digital metadata journaling system for better data recovery and ensuring file integrity. If your ReFS volume becomes inaccessible following an update, this article provides helpful solutions.

Many users experience this problem after executing Windows updates or upgrading their systems from Windows 10 to Windows 11. The main reasons behind this issue include:
- Incompatible or Corrupted Volume: If the recent update (or OS upgrade) does not align with the disk volume, the file system may struggle to read or write data effectively. Interruptions during the update process or errors can also render the volume inconsistent, leading to inaccessibility.
- Hardware Problems: Physical issues with the hard drive may result in inaccessible sectors, damaging the file system’s metadata. Given that ReFS relies heavily on this metadata, such hardware failures can compromise file locations and attributes, causing the volume to become inaccessible.
- Corrupted ReFS Metadata: Damage to or misalignment of the metadata structure may arise from unexpected system shutdowns, hardware malfunctions, or software bugs. In these situations, the file system may be unable to access or manage the stored data, triggering the accessibility error.
Resolving Inaccessible ReFS Volume After Update
You can follow these steps to address the issue:
- Uninstall the most recent Windows update
- Update the ReFS volume to the latest version
- Activate Integrity Streams
1] Uninstall the Most Recent Windows Update
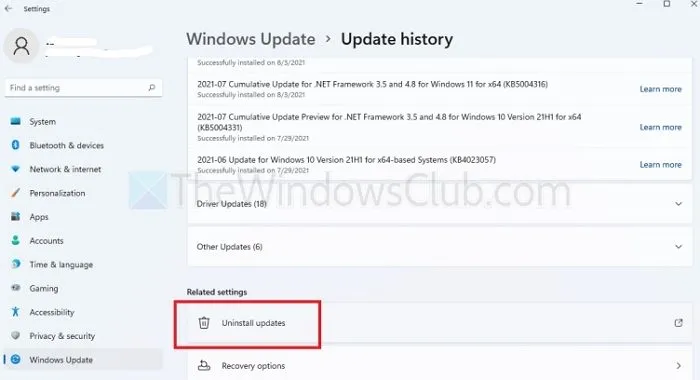
- Press the Windows + I keys simultaneously to access the Settings application.
- From the left pane, choose the Windows Update option, then click on Update History on the right side.
- In the Related Settings section, select Uninstall updates and click on Uninstall next to the update you wish to remove.
- Once the uninstallation is finished, restart your computer.
2] Update the ReFS Volume to the Latest Version
If your system is using an outdated version of ReFS, it may not be compatible with your current version of Windows. For example, the ReFS 1.x support is no longer provided in Windows. In such cases, upgrading ReFS may resolve the issue. You can perform an in-place upgrade as follows:
- Download the Windows 11 ISO file.
- Open the downloaded file and initiate the setup file to proceed.
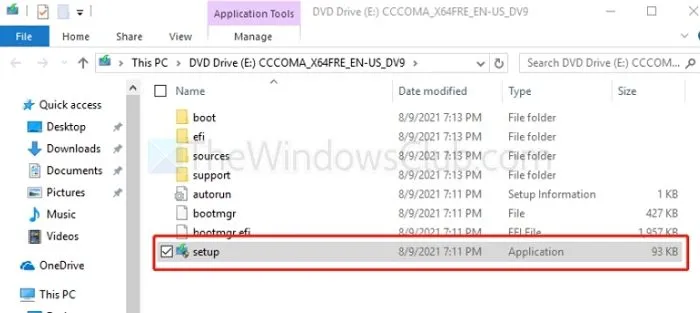
- Select Next to continue and follow the on-screen prompts to complete the update.
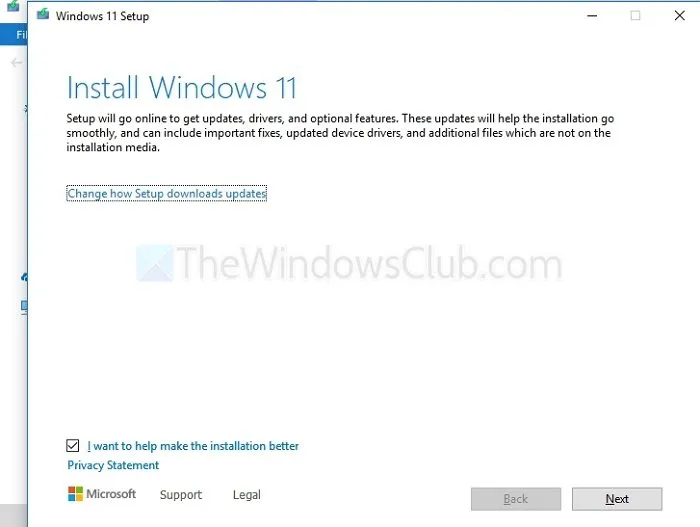
- After the process concludes, verify the current version of ReFS by using the fsutil command in the Windows Terminal. Open it as an administrator and enter:
fsutil fsinfo refsinfo X
3] Enable Integrity Streams
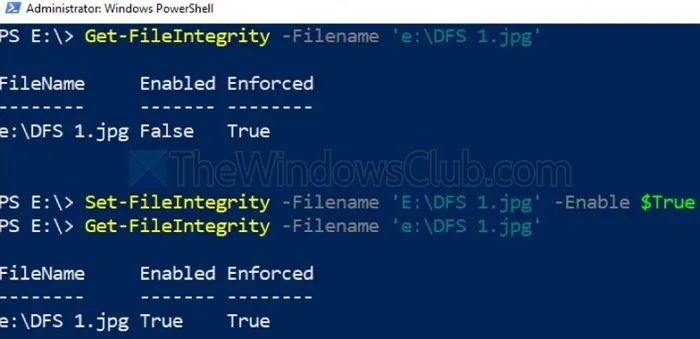
Integrity Streams can detect and repair damaged sections if the ReFS volume is inaccessible due to data corruption following Windows updates. This tool is essential for restoring the disk volume’s functionality and safeguarding your data. To use this feature:
- Launch the Windows Terminal by typing cmd in the Desktop Search Bar, then run it as an Administrator.
- Execute the following commands in the specified order:
Set –FileIntegrity –Filename 'E:\DFS 1.jpg' –Enable $True
Get –FileIntegrity –Filename 'E:\DFS 1.jpg'
The first command activates File Integrity for all new files, while the second command applies it to existing folders and subfolders.
How Does NTFS Differ from ReFS?
NTFS modifies file metadata directly, which can lead to data loss or corruption during system crashes. In contrast, ReFS prioritizes data integrity by creating a backup of the metadata before making any changes, only linking the data to the updated metadata once it is securely written to disk.
Is ReFS Quicker than NTFS?
In terms of performance, ReFS typically outshines NTFS, especially in extensive environments and during heavy workloads. This advantage stems from its efficient handling of metadata, where it retains a copy prior to editing, thus reducing the risk of data corruption and enhancing overall performance.
Leave a Reply