Troubleshooting: ERROR_NOT_REDUNDANT_STORAGE 333 (0x14D) Solutions
The ERROR_NOT_REDUNDANT_STORAGE, identified by the code 333 (0x14D), typically arises when the disk in question lacks redundancy, thus raising concerns over potential data loss. The error message indicates that the storage device does not offer redundancy.
Before diving into the solutions, it’s essential to determine if the issue originates from Storage Spaces or RAID configurations. Consider resetting or rebuilding those systems. If you are dealing with external hard drives, simply reconnecting them might resolve the issue!
How can I resolve ERROR_NOT_REDUNDANT_STORAGE?
1. Update Your Disk Drivers
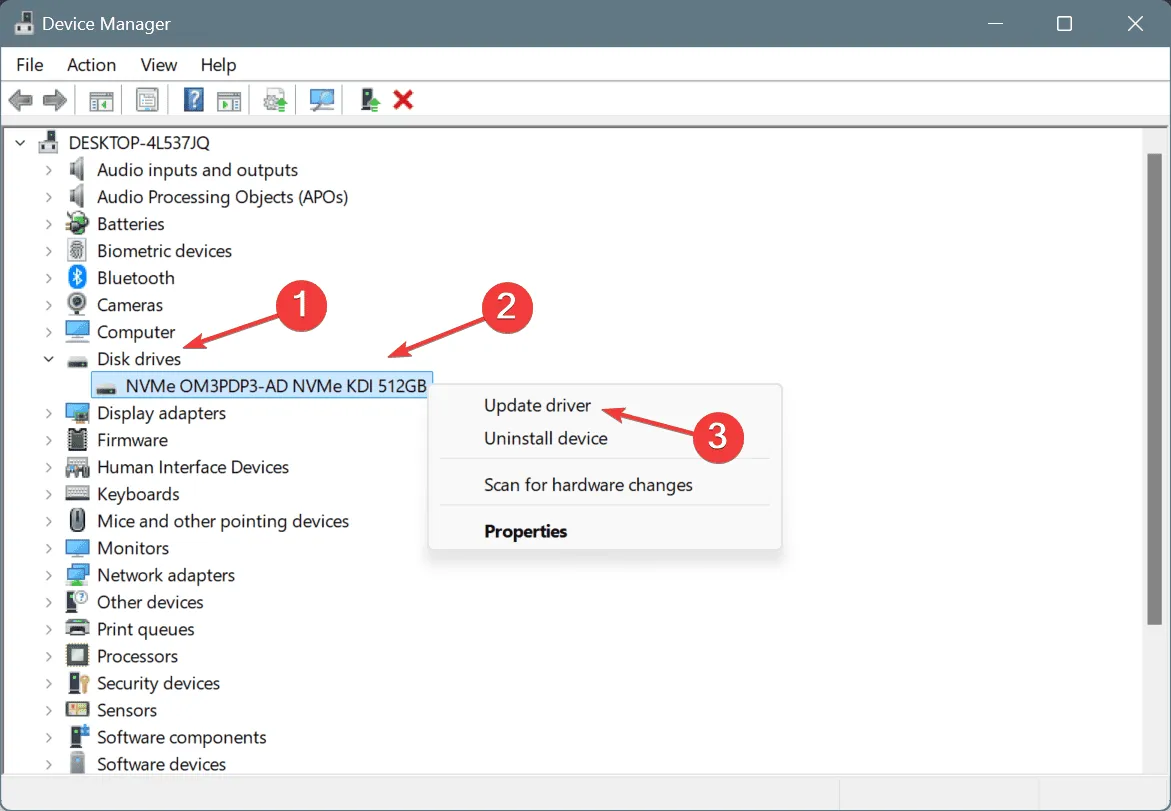
- Press Windows + X to access the Power User menu, then click on Device Manager.
- In the Disk drives section, right-click on the drive that is causing the error and select Update driver.
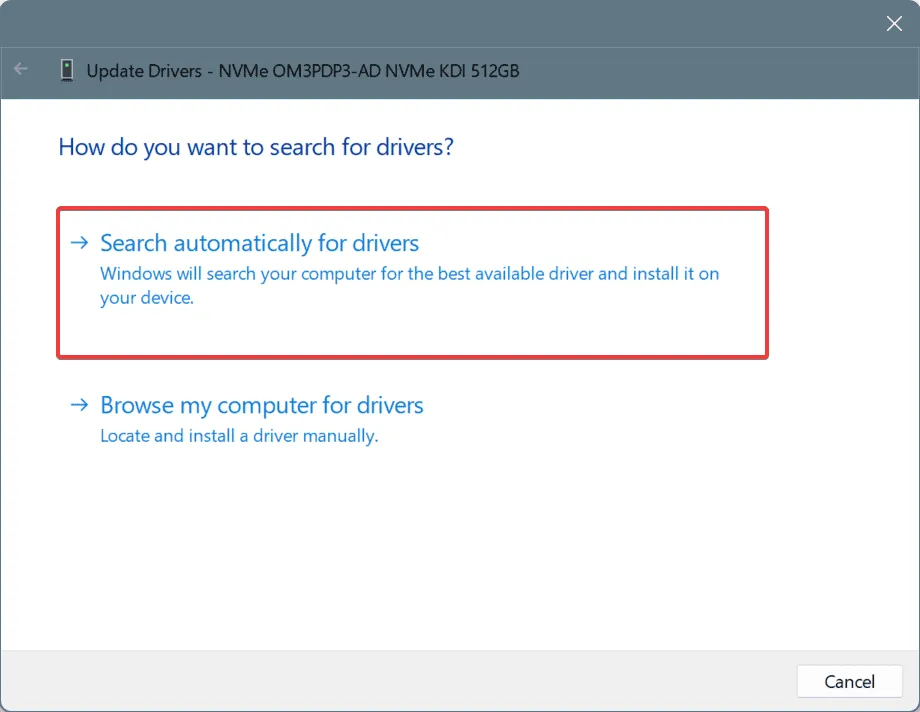
- Select Search automatically for drivers and wait while Windows installs the most suitable local version.
- Restart your computer to apply the updates and check if the issue persists.
Having outdated or faulty disk drivers can trigger the ERROR_NOT_REDUNDANT_STORAGE message indicating that the storage device lacks redundancy. By updating your drivers, you should be able to resolve the issue quickly.
If an updated driver isn’t found automatically, visit the manufacturer’s website to download and install the latest version manually!
2. Execute a Check Disk
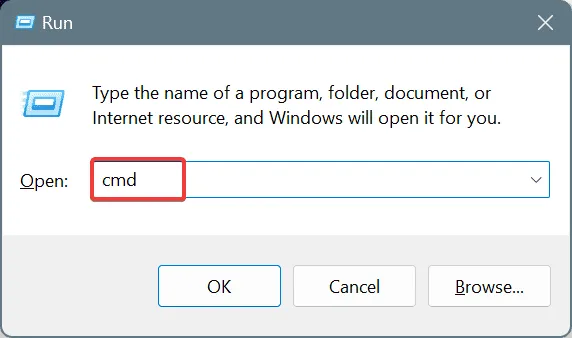
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog, type cmd, then press Ctrl + Shift + Enter .
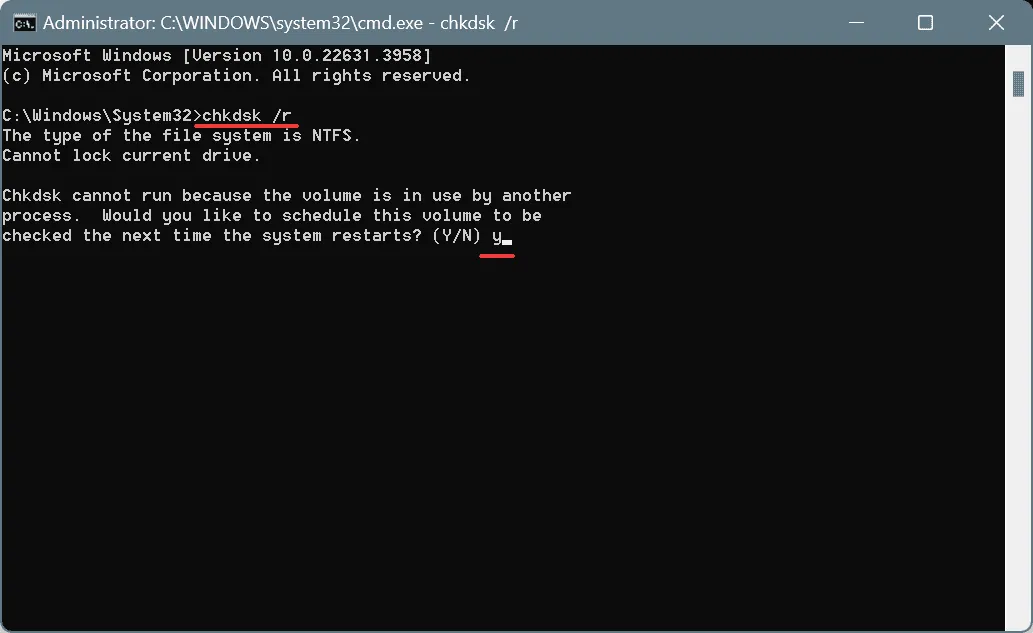
- Choose Yes when prompted by the User Account Control (UAC).
- Enter the following Check Disk command and hit Enter:
chkdsk /r - If prompted to schedule the scan for the next system restart, type Y and hit Enter to confirm.
- Now, restart your computer and allow Check Disk to proceed.
The built-in Check Disk tool can detect and correct various disk-related problems, including addressing ERROR_NOT_REDUNDANT_STORAGE 333 (0x14D)!
3. Repair Corrupted System Files
- Press Windows + S to open Search, type Command Prompt, and select Run as administrator.
- Click Yes when prompted by UAC.
- Input these DISM commands one at a time, pressing Enter after each:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth,DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth,DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth - Next, run this SFC command:
sfc /scannow
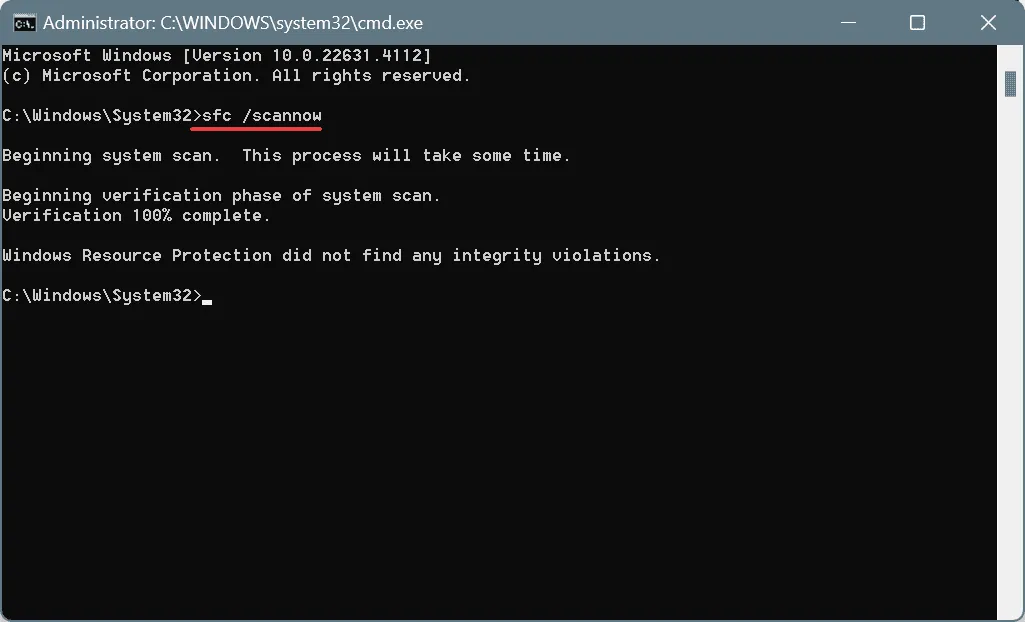
- Finally, restart your computer to see if the issue is resolved.
In many instances, ERROR_NOT_REDUNDANT_STORAGE can result from corrupted system files. Performing DISM and SFC scans can help replace damaged files with their cached versions!
4. Remove Conflicting Applications
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog, type appwiz.cpl, and hit Enter.
- Select any recently installed application from the list and click on Uninstall.
- Follow the prompts provided to complete the uninstallation process.
- Restart your computer and see if the issue has improved.
If the error remains even after uninstalling the latest apps, it may be due to leftover files and registry entries. In this case, consider using a reputable uninstallation tool to remove any remnants of the program!
5. Conduct a System Restore
- Press Windows + S to open the Search function, type Create a restore point, and select the appropriate result.
- Click the System Restore button.
- If applicable, choose the Choose a different restore point option, then click Next.
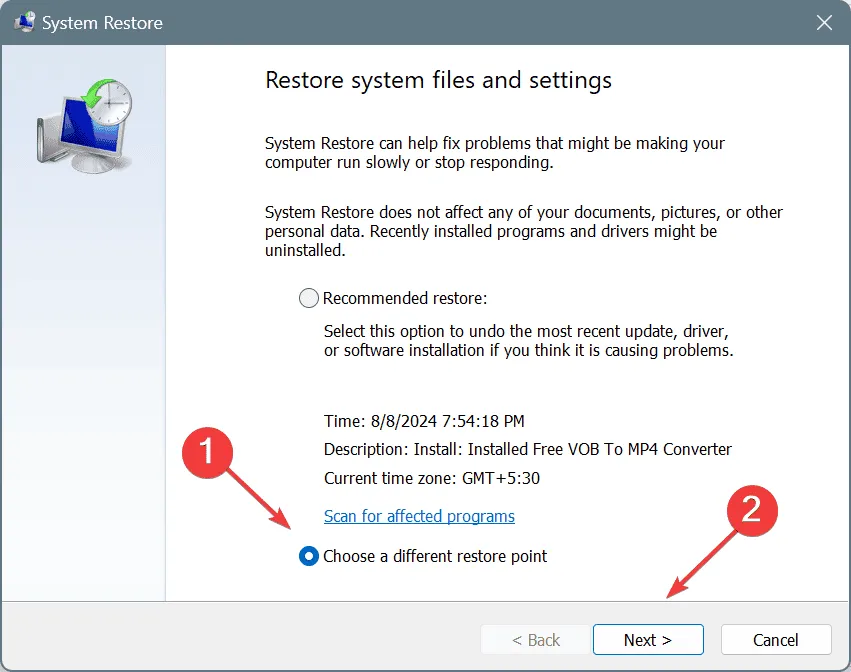
- Select the oldest restore point or one created prior to noticing the issue, then click Next.
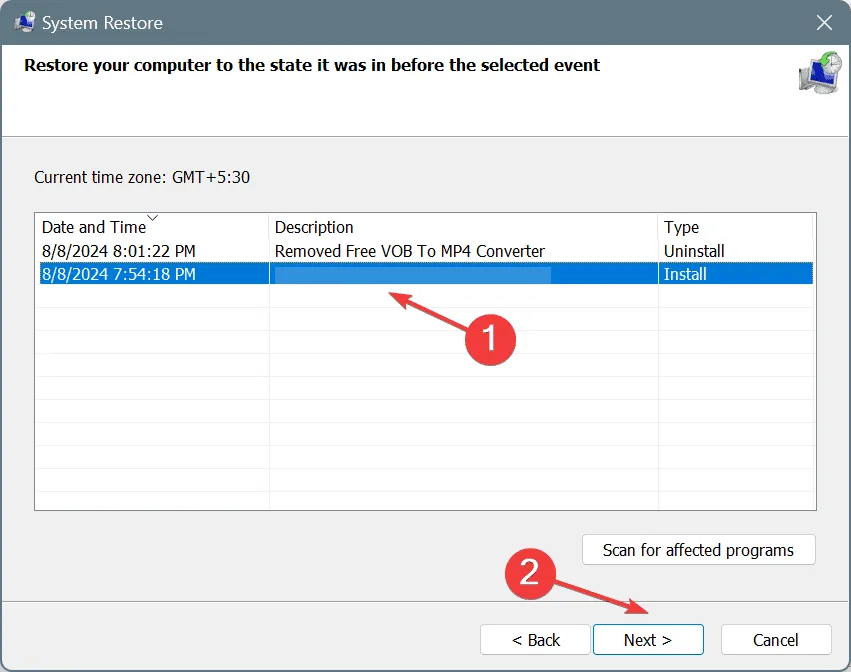
- Verify the information, click Finish, and confirm your selection.
- Wait for the restoration process to finish, which usually takes about 15 to 30 minutes.
When all else fails, a system restore may be the solution to rectify ERROR_NOT_REDUNDANT_STORAGE by reverting any recent changes that initiated the problem. Just ensure you select a restore point that predates the issue.
Which of these solutions resolved your issue? Feel free to share your experience with our readers in the comments below!
Leave a Reply