Step-by-Step Guide to Configuring a Domain Controller in Windows Server
Establishing a Domain Controller (DC) on a Windows server is fundamental for overseeing a secure and centralized network. A Domain Controller is essential for handling authentication requests, enforcing security protocols, and facilitating the management of users and devices within an Active Directory Domain.
Understanding the Role of a Domain Controller in Windows Server
A Domain Controller (DC) in Windows Server serves as a server that responds to security authentication requests across a Windows domain. It plays a vital role in safeguarding network security and managing user access. The DC not only verifies user credentials during network logins but also assists in assigning resources depending on user needs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up a Domain Controller in Windows Server
If you’re ready to set up a Domain Controller (DC) on your Windows Server, follow these steps:
- Check that all prerequisites are fulfilled
- Install the Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS)
- Promote the server to function as a Domain Controller
- Confirm the Domain Controller’s configuration
Now, let’s dive into the detailed procedure.
1] Check Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the installation and configuration of a Domain Controller on your Windows server, it’s essential to confirm that certain basic requirements are met. This includes ensuring that Windows Server is installed and configuring a static IP address for the server. Once these prerequisites are satisfied, you can begin the installation of Active Directory Domain Services.
2] Install Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS)
Once you have verified the prerequisites, the first step in setting up your Domain Controller involves installing Active Directory Domain Services. There are three main methods to install ADDS on a Windows Server: through the Server Manager, Windows PowerShell, or Command Line. In this guide, we will utilize the Server Manager to complete the installation. Here’s how:
- Log into the Windows server using an administrator account.
- In the Server Manager dashboard, navigate to Dashboard > Manage, then click on Add Roles and Features, followed by the Next button.
- Choose ‘Role-based or feature-based installation’, select a server from the server pool, choose the host to which you wish to add services, and click the Next button.
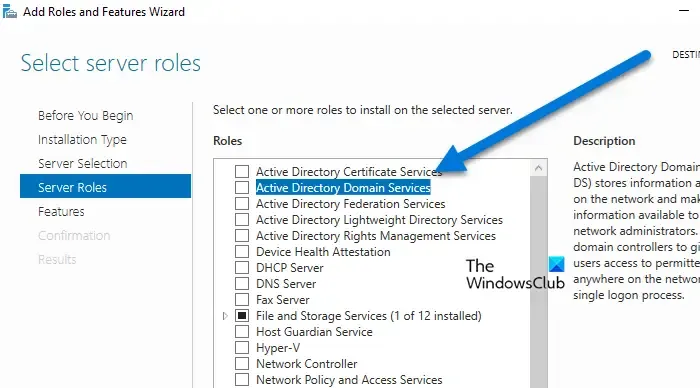
- Check the box for Active Directory Domain Services, then click the Add Features button on the subsequent page and hit Next.
- Accept the default features selected by clicking Next twice before finally clicking the Install button.
Allow time for the system to install the necessary features, and proceed to the next step when completed.
3] Promote the Server to a Domain Controller
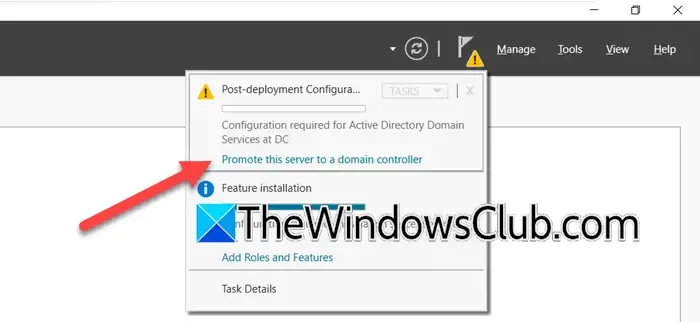
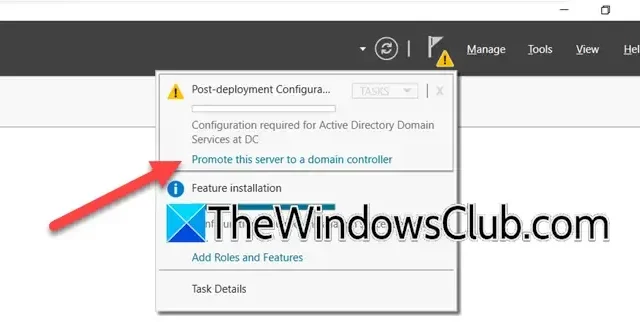
After successfully installing the ADDS roles and features, the next step is to promote the server to a Domain Controller. Here’s how to do it:
- Post-installation, click the notification that reads ‘Promote this server to a domain controller’, and select the ‘Add a new forest’ option as your deployment type.
- For the new domain setup, input a Root Domain Name, click Next, and select the Functional Level for Forest and Domain. Since this is your primary DC, ensure that the boxes for DNS server and Global Catalog are checked, leave Read-only Domain Controller unchecked, and enter a password for Directory Services Restore Mode.
- Click Next, confirm the NetBIOS name, hit Next again, and specify the paths for the database, log files, and SYSVOL.
- Lastly, review your configuration settings and click Next, followed by the Install button.
Your server will automatically restart once the installation is complete.
4] Validate Domain Controller Configuration
After your server has rebooted, log in with your domain credentials and ensure that Active Directory is operating correctly. To check this, run the DCDIAG command or open Server Manager, then navigate to Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers. You can also run nslookup using your domain name to verify DNS functionality.
To implement Group Policies (GPOs) for managing settings across your domain, access this feature via Tools > Group Policy Management, where you can right-click on the domain or an Organizational Unit to create or edit a GPO for centralized management.
Your Domain Controller is now set up to manage users, computers, and other resources within the domain.
How to Assign a Domain to a Windows Server
To assign a domain to your Windows server, navigate to Server Manager, install Active Directory Domain Services, and subsequently promote the server to act as a Domain Controller. You can either create a new domain or utilize an existing one and then reboot the server to apply all changes. A comprehensive explanation of this procedure is discussed above.
Differences Between Active Directory and Domain Controller
Active Directory is a Microsoft service designed to store and manage information about network resources like users, computers, and groups, facilitating centralized management and security. In contrast, a Domain Controller is a server that hosts Active Directory and oversees network authentication. Essentially, Active Directory serves as the system, while the Domain Controller functions as the server running the service, making them inherently interconnected.


Leave a Reply