Top 6 Methods to Monitor Hard Disk Health on Windows


Replacing most PC components is straightforward, but the critical data on your hard drive is irreplaceable without a backup. Regularly check your hard disk health using both built-in and third-party tools to stay prepared.
Early Signs Hard Drive Is Failing
Before your hard drive health starts to decline, you’ll often notice early warning signs. These indicators may surface just weeks before a drive failure, so it’s vital to act quickly and back up your data consistently. Watch for the following early signs while checking your hard disk:
- Longer boot times
- Frequent system crashes
- Regular appearances of the Blue Screen of Death
- BIOS errors during startup
- Missing files, indicating failing segments
- Increased file load times in File Explorer
1. Check Hard Disk Health From the BIOS
Your PC’s BIOS contains various built-in tools, including a hard disk health checker. Restart your PC and press Delete, F2, F12, or the key shown on your boot screen to enter the BIOS. Alternatively, you can set Windows to boot directly into the BIOS.
Inside the BIOS, the instructions differ based on the motherboard manufacturer. For example, on an MSI Mortar Wi-Fi B550M, go to Settings -> Advanced -> NVME Self-Test to check NVMe drive health.
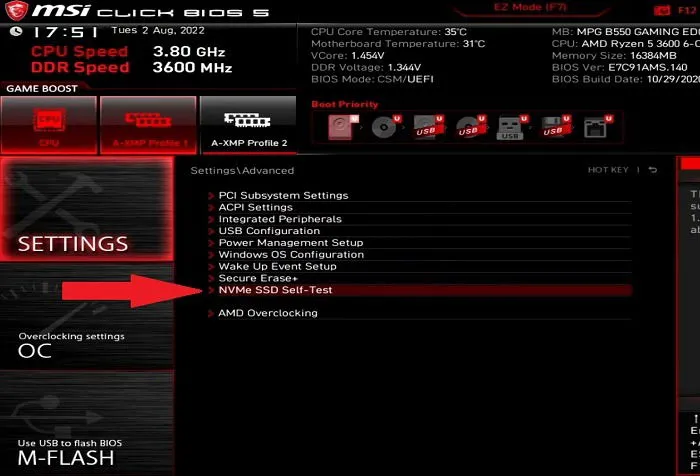
On newer HP laptops, use a separate UEFI diagnostic tool by pressing F2 during boot, then navigate to Component Tests -> Hard Drive to perform tests on your drives.
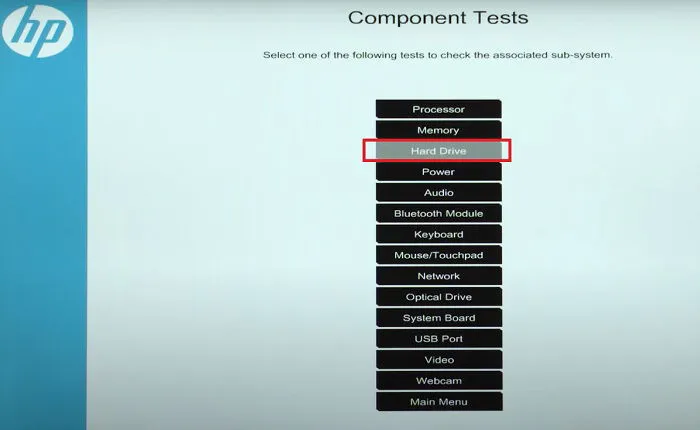
The BIOS also provides a way to confirm whether the hard drive is detected by your PC or motherboard.
2. Optimize and Defrag Your Hard Drive
Over time, both HDDs and SSDs can slow down. For HDDs, this is often due to fragmented files spread across various sectors, while SSDs experience different performance issues. It’s crucial to optimize both types of drives periodically to enhance performance and extend lifespan.
Use the built-in Windows Defragment and Optimize Drives tool to analyze and optimize your drives. Access it by opening Start and searching for disk defrag. Select Defragment and Optimize Drives from the search results.
Choose your drive and click Optimize to begin scanning for fragmented files and to enhance the drive’s performance. Windows typically performs this operation automatically for SSDs regularly.
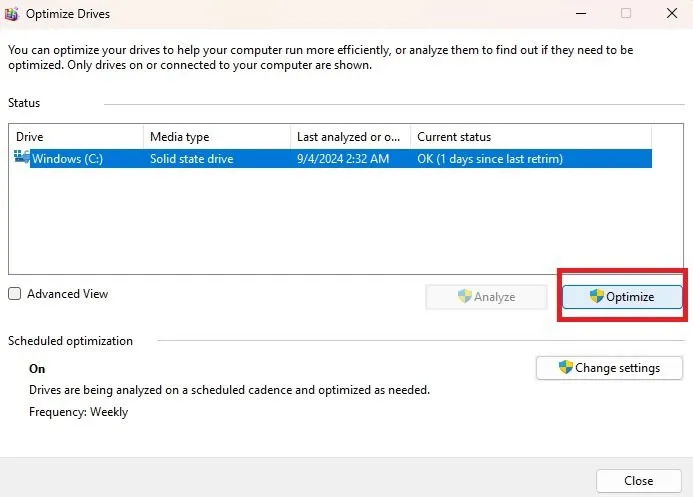
For HDDs, use best practices to defrag properly, while for SSDs, ensure you’re following optimization guidelines.
3. Use the HDD Manufacturer’s Tools
Many major hard drive manufacturers offer free tools to monitor hard drive health and performance. Start by identifying your hard drive’s make and model.
To find this, press Win + X and select Device Manager. Expand Disk drives and note your hard drive’s model number.
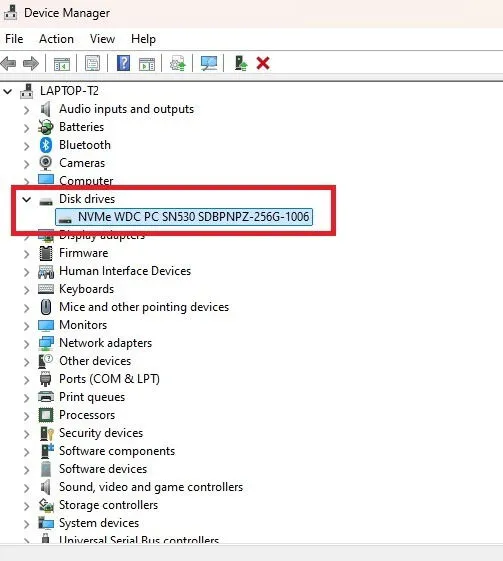
After identifying the manufacturer, search their website for the appropriate hard drive utility.
Here are some relevant download links for popular hard drive brands:
- Western Digital
- Seagate (compatible with most hard drive brands)
- Samsung
While the tools may vary in functionality, they all provide essential diagnostic features to assess your hard drive health.
4. Use Windows CHKDSK Tool
The Windows CHKDSK tool scans your hard disk for system errors and bad sectors, offering insights into hard disk health. It can also fix issues (when possible) and alerts you to any significant problems that cannot be resolved.
To use CHKDSK, open Start, type cmd, and select Run as administrator for Command Prompt.
Type in chkdsk and press Enter to execute a basic scan.
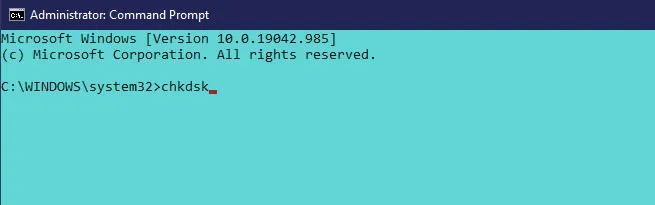
For a more thorough scan, use chkdsk /f /r to address bad sectors and recover readable data. Alternatively, chkdsk /f /r /x dismounts the drive before scanning. Microsoft provides a list of parameters for CHKDSK to assist in checking your hard disk health.
5. Use WMIC to Check Hard Disk Health
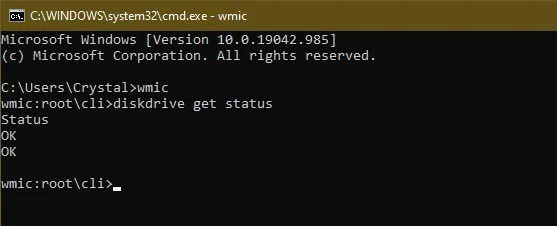
WMIC is a command-line tool allowing you to perform various administrative tasks, including hard disk health checks. It utilizes the S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) feature to assess and provide a straightforward status report, such as “OK” or “Pred Fail.” This basic tool offers valuable insight.
To use WMIC, press Win + R to open the Run dialog, type cmd, and click OK to launch Command Prompt.
Type wmic and press Enter. Once the WMI interface is active, type:
Press Enter again to view your hard disk’s status.
6. Use a Third-Party Hard Disk Health Checking Tool
Third-party tools can provide a comprehensive check of hard disk health, offering more detailed information than a simple good or bad status. These tools also leverage the S.M.A.R.T. feature of hard disks for insights.
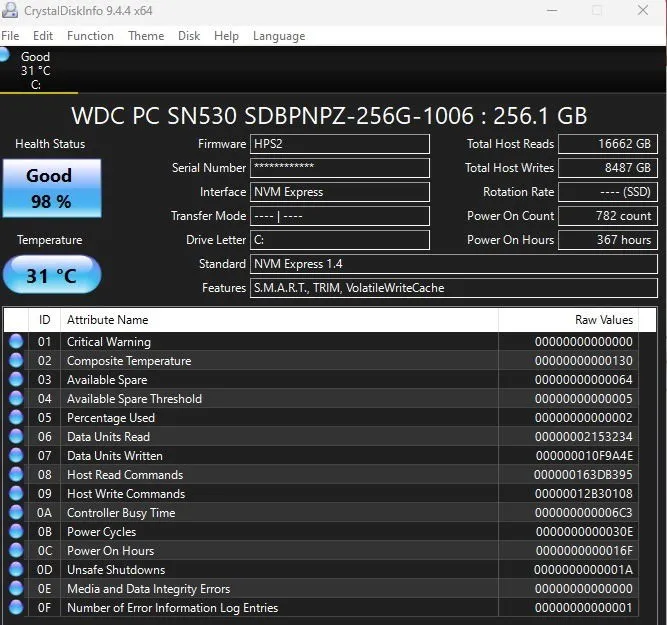
CrystalDiskInfo
CrystalDiskInfo is a powerful, free tool that provides various details, including temperature, health status, drive type, and attributes like read/write error rate and spin-up time. It also features various themes to enhance the user experience.
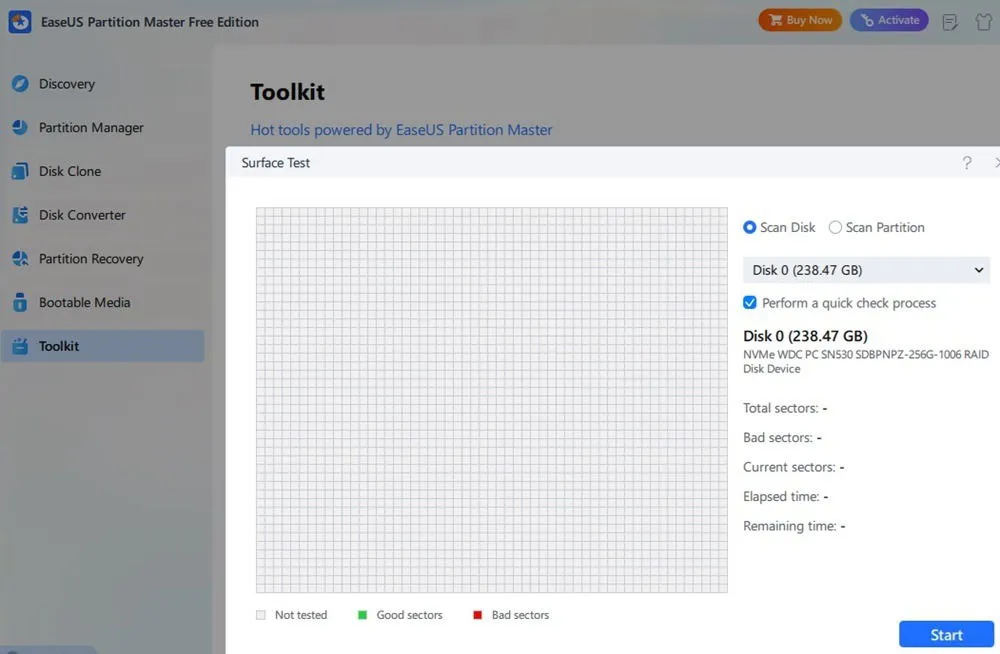
EaseUS Partition Master
The free version of EaseUS Partition Master includes a host of partitioning tools, along with Bad Sector Scan and MBR Rebuild functions to check hard drive health. Although it has a premium version with advanced features, the free version suffices for basic health checks.
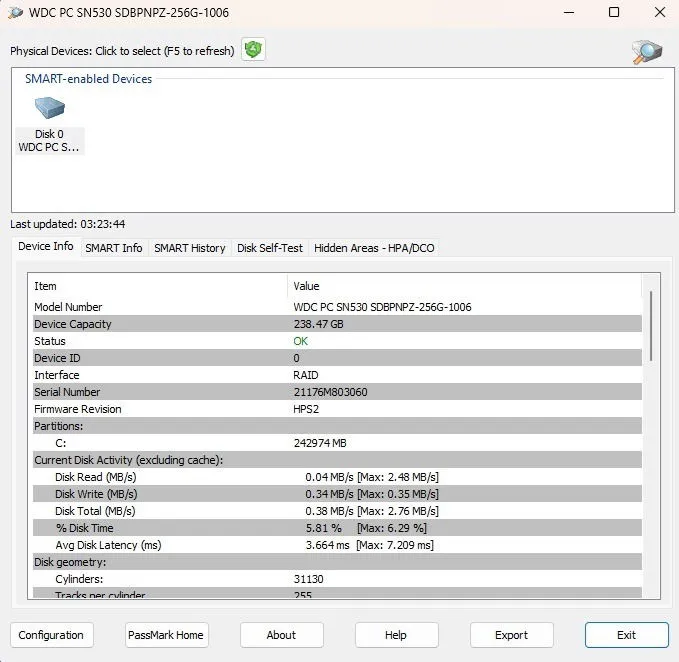
PassMark DiskCheckup
DiskCheckup from PassMark provides extensive information beyond what EaseUS offers. This lightweight, free tool shows various S.M.A.R.T. attributes such as temperature, spin-up time, operational hours, endurance, and more, with thresholds indicating if elements are outside normal ranges.
What Should I Do If My Hard Drive Is Failing?
While these methods are useful for assessing hard disk health, they do not resolve underlying issues. If you suspect problems, take immediate action.
- Back up all important files. If the hard drive shows significant issues, prioritize backing up critical files, as the drive may fail before a complete disk image can be created. Regular backups are essential, even with a functioning drive.
- Compile a list of installed software and product keys. Document everything you’ll need to reinstall, along with necessary product keys, to simplify the transition. Belarc Advisor can assist, but creating a complete disk image is preferable.
- Save work frequently. If you are using a failing drive, save your work to an external storage device or cloud service to preserve your data.
- Prepare a replacement drive or device. You can either purchase a new hard drive to install in your computer if it’s relatively new, or consider investing in a new system altogether.
Another option is to remove the faulty drive and use a USB or external hard drive for your operations. This allows data accessibility across different computers. Check out these top Linux distros for setups similar to Windows.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do hard drives typically last?
Mechanical hard drives generally last between three to five years, although careful handling can extend their lifespan. SSDs usually last around ten years. However, hardware can fail unexpectedly, sometimes earlier than anticipated.
How can I prolong my hard drive’s lifespan?
If you are using an HDD, handle it with care, particularly while it is in operation. Dropping your laptop or exposing it to shocks can damage the drive. Additionally, ensure your PC is well-ventilated to prevent overheating, which can lead to premature drive failure.
While manufacturing defects are unavoidable, treating your PC with care can help extend your hard drive’s lifespan by a year or more. If you notice issues, it’s imperative to back up your data and find a replacement.
Can I check the health of my external drives as well?
Yes, most of the tools mentioned can check the health of external hard drives since they can fail just like internal ones. Regular health checks on external drives help ensure you don’t lose valuable backup data unexpectedly. For testing SD cards, consider using specialized tools.
Image credit: Unsplash. All screenshots by Crystal Crowder.


Leave a Reply