How Many Processes Should Be Running on Windows 11?

Windows 11 is a great operating system, but it can sometimes run slowly and just not work as well as it should. If you’re experiencing performance issues, it could be the number of processes you have running.
One of the easiest ways to optimize your system is by adjusting how many processes are running on your machine at any given time. If you’ve ever had a computer freeze or crash because it was running too many programs at once, this article is for you.
What background tasks can I close?
Background tasks run in the background on your device and are important because they help keep your system stable. They include updates, syncing, and other services.
While some background tasks can be useful, others take up space on your computer without providing any real benefit.
The background tasks you can close will vary for every user. Taking an example from our PC at this time, the CTF Loader was one of our culprits.
This service offers support for alternative input methods such as speech recognition and text translation. Since we only use the keyboard and mouse, it is an unnecessary task hence the need to disable it.
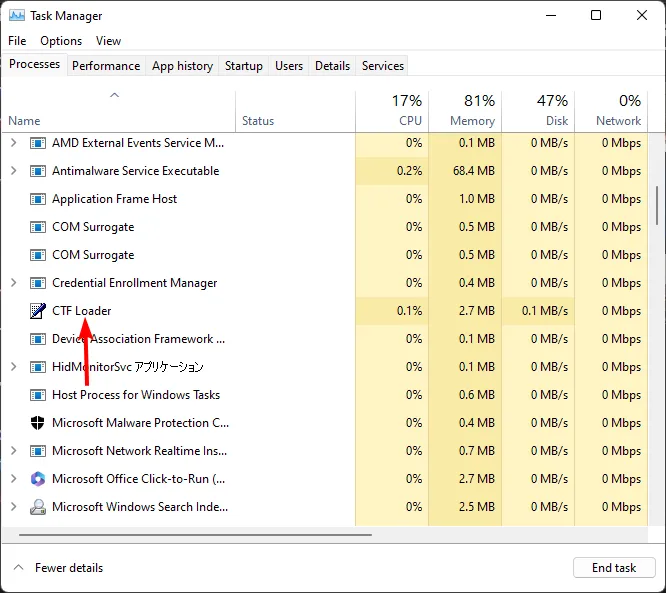
If you have a lot of apps that are running in the background, you should check what they are doing. This will shed more light on which ones you should disable. So, How do I determine which programs should be closed?
The goal is to find the right balance between keeping your computer running smoothly and keeping it safe.
You can determine which programs to close by looking at each program’s CPU and memory usage. The programs you should close are those that have been running for a long time and have not been used recently.
If a program is running, and you’re not using it, it takes up memory and processor resources for no reason.
You can single out as many but be careful about closing critical tasks that keep Windows running. Sometimes, your CPU may be 100% even when no program is running, so address such issues first.
How many background processes are normal?
The number of processes running on your computer will vary depending on the applications being used, configuration, and hardware. In general, you should have no more than 50 or 60 processes running at any given time.
Other factors that affect the number of processes running include:
1. Amount of RAM
Of course, this will depend on how much RAM you have. The more RAM your computer has, the more processes can run simultaneously. RAM is fast and temporary storage.
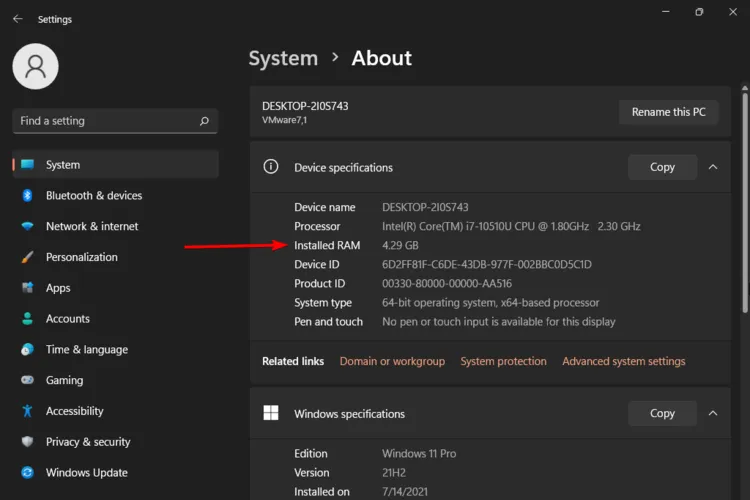
It’s where programs store the data they need to work with while running. The more RAM you have, the more programs can be opened at once without slowing down your computer.
2. Type of processor
The number of processes a CPU can run will depend on the type. In general, faster processors can handle more processes at once than slower processors. However, the number of cores in a processor also plays a significant role.
For example, if you have a single-core processor, only one process can run at a time. If you have a dual-core processor, then two processes can run simultaneously, and so on.
3. Processor speed
The speed of your CPU determines how quickly it can process instructions and execute tasks. If your CPU is slower, then it will take longer for each instruction to complete.
This means that if two PCs are running the same program at different speeds, the slower computer will take longer to complete each instruction because it takes longer for each instruction to be processed by the CPU.
4. User activity
The more user activity there is on your computer, the more likely it is that more than one process will run at any given time.
For instance, the average user who performs light tasks on the internet will typically have at least a dozen different processes running in the background simultaneously.
On the other hand, someone who is a heavy user who frequently plays games, edits videos, and uses different apps may see well over 100.
The number of processes running on your computer can be a useful indicator of your system’s performance. It also provides an indication of how much processing power they require.
You can end the tasks or limit the process’s CPU usage. This will free up some memory and boost your PC’s speed.
How do I reduce the number of processes running in Windows 11?
To keep the number of processes open on your PC to a minimum, follow the steps below:
Avoid opening too many programs
The more programs you open at once, the more resources each one will take up, especially if running in the background.
So limit yourself to five or six instead of having 20 browser tabs open simultaneously. Once you’re done, close and open more.
Clear your hard drive
If your hard drive is full, Windows will need more memory to temporarily store files until they can be written to the hard drive. This makes it slower and uses more power than necessary.
Defragmenting your hard drive will make it faster, but it won’t reduce the number of processes running in Windows.
Uninstall unnecessary apps
You may have installed some apps you don’t use anymore or more than one app that does the same thing. Try uninstalling these apps to free some hard drive space.
Unnecessary apps can use up CPU resources and drain your battery. If possible, try using web versions of apps you don’t use regularly.
Disable startup apps
- Press the Windows key + X and select Task Manager to open the Processes tab.
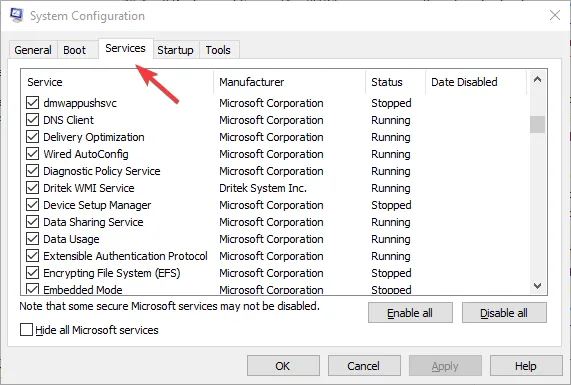
- Select the Start-up tab.
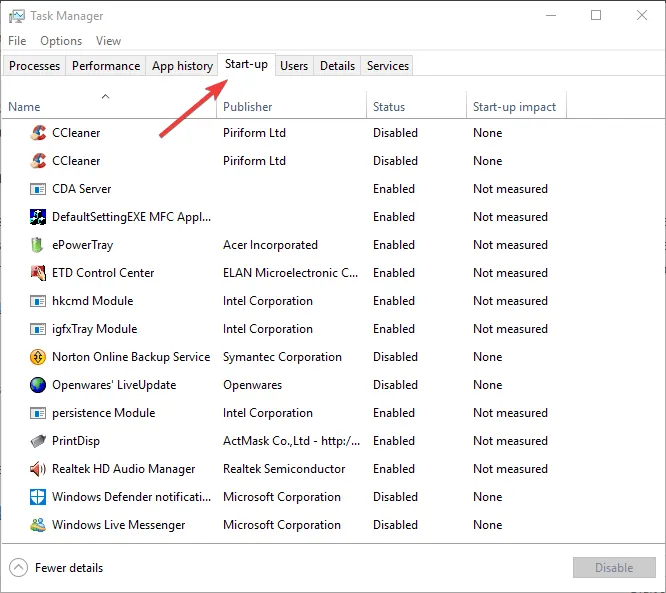
- Select any non-essential program and press the Disable button to remove it from the Windows Startup.
The fewer startup programs you have, the faster your boot time. Hopefully, you now know how many processes you should have running on your Windows 11.
We’d love your feedback on some of the background services you have disabled and why you think they’re unnecessary.


Leave a Reply